Networking Models
One other important benefit of layering is that it makes it possible for technologies defined by different groups to interoperate. For this to be possible, it is necessary for everyone to agree on how layers will be defined and used. The most common tool for this purpose is a networking model. The model describes what the different layers are in the network, what each is responsible for doing, and how they interact. A universally-accepted model ensures that everyone is on the same page when creating hardware and software.
The most common general model in use today is the Open Systems Interconnection (OSI) Reference Model, which concepts of seven stacked layers. These range from the Physical Layer (layer one) at the bottom, which is responsible for low-level signaling, to the Application Layer (layer seven) at the top, where application software is implemented. Understanding the OSI model is essential to understanding networking as a whole. I explain models and layers in more detail, as well as providing a complete description of the OSI Reference Model, in its own dedicated section.
Networking ArchitecturesClosely related to the concept of a model is that of an architecture. An architecture is essentially a set of rules that describes the function of some portion of the hardware and software that constitute a stack of layers. Such a rule-set usually takes the form of a specification or standard that describes how equipment and programs using the technology must behave. A networking architecture is designed to implement the functions associated with a particular contiguous set of layers of the OSI Reference Model, either formally or informally.
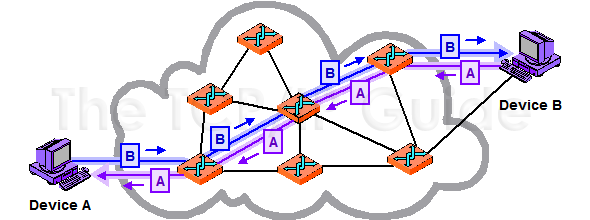
In this Guide we are, of course, interested in the TCP/IP protocol suite, which runs the Internet, and a complex set of technologies that spans many layers of the OSI model. It is by examining the various components of TCP/IP and how they implement different OSI model layers that we will really learn how TCP/IP works. For starters, the name of the suite, TCP/IP, comes from the Transmission Control Protocol (TCP), which operates at layer four of the OSI model, and the Internet Protocol (IP) that runs at OSI model layer three. IP provides services to layer four and uses services of layer two below it. TCP uses IP's functions and provides functions to the layers above it. The complete examination of TCP/IP starts by looking at its architecture and a second, special model that was developed specifically to make sense of TCP/IP.